Arnold Chiari Malformation – Atypical
Arnold Chiari Malformation or ACM is the unusually undersized growth of the lower back side of the skull resulting in lesser space for the other brain constituents in that region. As a consequence the mid brain, medulla, pons and cerebellum are cramped in close to each other thus pressing down on to the spinal cord line. This swarming hinders the regular operations of the brain and at times spinal cord components. Additionally, the movements of the CSF (cerebrospinal fluid) could be obstructed which creates augmented pressure in the brain and at times in the region of the spinal cord.
CSF is formed in the brain cavity, bathing the brain surfaces as well as the spinal cord and functions as a shock-absorbing agent and is required for appropriate operations. The CSF is taken up by the body at the base portion of the spinal cord.
Arnold Chiari Malformation is of 3 forms:
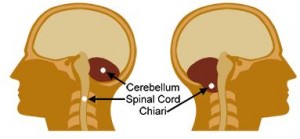 ACM I
ACM I
It is typified by brain tissue protruding beneath the aperture of the skull base and could comprise an irregular liquid blister-similar cavity known as syringomyelia and more than normal CSF accruement or hydrocephalus.
ACM II
It is a protuberance of brain stem as well as cerebellar brain tissue via the aperture in the skull. This type of irregularity could develop alongside hydrocephalus and syringomyelia, however, additionally; it is mostly linked with spina bifida (an inborn disorder wherein the vertebrae are incapable of totally encircling the spinal cord).
ACM III
ACM III would comprise of all the traits mentioned in I as well as II and additionally a protuberance of spinal cord caused due to a pouch or balloon-similar irregularity (myelomeningocele) which could be containing CSF and at times problem from the spinal cord casings.
Symptoms of Arnold Chiari Malformation
The cerebellum conveys data to the body regarding preservation of balance, regulating muscular tensions and coordinating limb control. Compression of cerebellum and adjacent tissues would possibly be resulting in headache, giddiness, neck aches, weariness, rigidity, puking, problems in ingestion, suffocation, weakened facial and head muscles, discomforting sensations in the arm and leg area and varied levels of mental impediment.
Signs and symptoms of Arnold Chiari Malformation generally are apparently soon following delivery. In case symptoms fail to become apparent in infancy, individuals having ACM might exhibit signs of deteriorating mental impediment during teen years or adulthood. This mostly becomes noticeable as instinctive, swift downwards eye motions, additionally giddiness, headaches, dual eyesight, auditory ringing, uncoordinated movements and abrupt pains felt in the area around the eyes.
Causes, Commonness and Risk Factors
The precise cause of ACM is still unclear. What is the reason for unusual skull development is not yet known. Several investigators doubt that ACM is heritable however persuasive proof is still missing. Arnold Chiari Malformation commonness and occurrence rates are tricky to approximate since it is not a citable condition and since populace-based researches have not yet been performed for ascertaining the true rate of incidence. ACM is an uncommon condition though it deemed an inherited irregularity it could develop later on during life subsequent to a mishap or due to unidentified means.
Treatment
Though therapy choices are quite few and solely surgical intervention could cause enlargement of the region and facilitate greater space for the cerebellum and other tissues. This is performed by removal of a section of the lower portion of the skull at the backside of head and maybe by removal of some of the upper parts of the vertebra in the spinal column. The extent of removal could not be ascertained till a detailed exam has been performed by a specialist in Chiari condition.
All surgical procedures carry risks and this kind of surgery is grave and must not be taken in a light vein. Mostly over one surgical procedure would be needed. In case symptoms could be managed then surgical procedure might not be suggested. But, in case symptoms become intolerable or the individual eventually shows mental deterioration or head/spinal cord pressure augments then surgery is presently the sole choice.
Prognosis
The more acute symptoms are, less favorable the prognosis. The signs and symptoms of majority of the people would show improvement with surgical procedure and several of them would experience least symptoms. In other cases, operative methods would be necessary. An acute ACM case in a child could be life-menacing.



